
Electrical Safety Program
Purpose
The Electrical Safety program is designed to prevent electrically related injuries and property damage. This program also provides for proper training of maintenance employees to ensure they have the requisite knowledge and understanding of electrical work practices and procedures. Only employees qualified in this program may conduct adjustment, repair or replacement of electrical components or equipment. Electricity has long been recognized as a serious workplace hazard, exposing employees to such dangers as electric shock, electrocution, fires and explosions. References: NFPA 70E, Electrical Safety Requirements for Employee Workplaces, National Electrical Code (NEC) and OSHA Standard (Electrical Safety) 29 CFR 1910.331 to 1910.339
Responsibilities
Management
Provide training for qualified and unqualified employees
Conduct inspections to identify electrical safety deficiencies
Guard and correct all electrical deficiencies promptly
Ensure all new electrical installations meet codes and regulations
Employees
Report electrical deficiencies immediately
Not work on electrical equipment unless authorized and trained
Properly inspect all electrical equipment prior to use
Hazard Control
Engineering Controls
• All electrical distribution panels, breakers, disconnects, switches, junction boxes shall be completely enclosed
• Water tight enclosure shall be used where there is possibility of moisture entry either from operations or weather exposure
• Electrical distribution areas will be guarded against accidental damage by locating in specifically designed rooms, use of substantial guard posts and rails and other structural means
• A clear approach and 3 foot side clearance shall be maintained for all distribution panels.
• All conduit shall be fully supported throughout it's length. Non-electrical attachments to conduit is prohibited.
• All non-rigid cords shall be provided strain relief where necessary.
Administrative Controls
• Only trained and authorized employees may conduct repairs to electrical equipment.
• Contractors performing electrical work must be hold a license for the rated work
• Areas under new installation or repair will be sufficiently guarded with physical barriers and warning signs to prevent unauthorized entry
• Access to electrical distribution rooms is limited to those employees who have a need to enter
• All electrical control devices shall be properly labeled
• Work on energized circuits is prohibited unless specifically authorized by senior facility management
• All qualified employees will follow established electrical safety procedures and precautions
Protective Equipment Controls
• Qualified employees will wear electrically rated safety shoed/boots.
• All tools used for electrical work shall be properly insulated
• Electrical rated gloves shall be available for work on electrical equipment
• Electrically rated matting will be installed in front of all distribution panels in electric utility rooms
Electrical Equipment
Examination
Electrical equipment shall be free from recognized hazards that are likely to cause death or serious physical harm to employees. Safety of equipment shall be determined using the following considerations:
• Suitability for installation and use in conformity with the provisions of this subpart. Suitability of equipment for an identified purpose may be evidenced by listing or labeling for that identified purpose.
• Mechanical strength and durability, including, for parts designed to enclose and protect other equipment, the adequacy of the protection thus provided.
• Electrical insulation.
• Heating effects under conditions of use.
• Arcing effects.
• Classification by type, size, voltage, current capacity, and specific use.
• Other factors which contribute to the practical safeguarding of employees using or likely to come in contact with the equipment.
Identification of Disconnecting Means and Circuits
Each disconnecting means for motors and appliances shall be legibly marked to indicate its purpose. Each service, feeder, and branch circuit, at its disconnecting means or overcurrent device, shall be legibly marked to indicate its purpose. These markings shall be of sufficient durability to withstand the environment involved.
A disconnecting means is a switch that is used to disconnect the conductors of a circuit from the source of electric current. Disconnect switches are important because they enable a circuit to be opened, stopping the flow of electricity, and thus can effectively protect workers and equipment.
Each disconnect switch or overcurrent device required for a service, feeder, or branch circuit must be clearly labeled to indicate the circuit's function, and the label or marking should be located at the point where the circuit originates. For example, on a panel that controls several motors or on a motor control center, each disconnect must be clearly marked to indicate the motor to which each circuit is connected. In the figure below, the Number 2 circuit breaker in the panel box supplies current only to disconnect Number 2, which in turn controls the current to motor Number 2. This current to motor Number 2 can be shut off by the Number 2 circuit breaker or the Number 2 disconnect.
All labels and markings must be durable enough to withstand weather, chemicals, heat, corrosion, or any other environment to which they may be exposed.
Definition of Terms
Qualified Worker: An employee trained and authorized to conduct electrical work.
Unqualified: Employees who have not been trained or authorized by management to conduct electrical work.
Training
Training for Unqualified Employees
Training for Unqualified Employees is general electrical safety precautions to provide an awareness and understanding of electrical hazards.
Electrical Safety Rules for Non-Qualified Workers
1. Do not conduct any repairs to electrical equipment
2. Report all electrical deficiencies to your supervisor
3. Do not operate equipment if you suspect and electrical problem
4. Water and electricity do not mix.
5. Even low voltages can kill or injure you
6. Do not use cords or plugs if the ground prong is missing
7. Do not overload electrical receptacles
Training for Qualified Employees
Training for Qualified Employees includes specific equipment procedures and requirements of Electrical Safety, 29 CFR 1910.331 to 1910.339
Training for employees (qualified and unqualified) who face a risk of electric shock that is not reduced to a safe level by proper electrical installation. Training can be either in the classroom or on-the-job type. The degree of training required is dependent upon the risk to the employee. Specific required training includes:
◦ Skills and techniques necessary to distinguish exposed live parts from other parts of electric equipment.
◦ Skills and techniques necessary to determine the nominal voltage of exposed live parts,
◦ Clearance distances specified in OSHA Standard 1910.333(c) and the corresponding voltages to which the qualified person will be exposed.
Personal Protective Equipment
Employees working in areas where the potential contact with exposed electrical sources are present and likely, will be provided and shall use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). The following rules apply to the use and care of PPEs:
1. PPEs shall be used where contact with exposed electrical sources are present and likely.
2. PPEs shall be designed for the work being performed and environment in which it is used.
3. PPEs shall be visually inspected and/or tested before use. Any defects or damage shall be replaced, repaired or discarded.
4. In cases where the insulating capabilities of the PPEs may be damaged during the work, a protective outer cover, such as leather, must be used.
5. Employees shall wear non-conductive head protection wherever there is a danger of injury from electrical burns or shock from contact with exposed energized parts.
6. Employee shall wear protective eye/face equipment whenever there is a danger from electrical arcs or flashes or from flying objects resulting from an electrical explosion.
Type of equipment | When to test |
|---|---|
Rubber insulating line hose | Upon indication that insulating value is suspect. |
Rubber insulating covers | Upon indication that insulating value is suspect. |
Rubber insulating blankets | Before first issue and every 12 months |
Rubber insulating gloves | Before first issue and every 6 months |
Rubber insulating sleeves | Before first issue and every 12 months |
Personal Protective Equipment
If slings are damaged or defective, they shall not be used. Until repairs are made on defective or damaged slings, they will be removed from service. If these slings are not repairable, they will be permanently removed from service. Appendix G lists the conditions that must be present to remove any sling from service.
Application of locks and tags.
A lock and a tag shall be placed on each disconnecting means used to deenergize circuits and equipment on which work is to be performed, except as provided for below.
1. The lock shall be attached so as to prevent persons from operating the disconnecting means unless they resort to undue force or the use of tools.
2. Each tag shall contain a statement prohibiting unauthorized operation of the disconnecting means and removal of the tag.
3. If a lock cannot be applied a tag may be used without a lock.
4. A tag used without a lock must be supplemented by at least one additional safety measure that provides a level of safety equivalent to that obtained by use of a lock. Examples of additional safety measures include the removal of an isolating circuit element, blocking of a controlling switch, or opening of an extra disconnecting device.
5. A lock may be placed without a tag only under the following conditions:
A. Only one circuit or piece of equipment is deenergized, and
B. The lockout period does not extend beyond the work shift, and
C. Employees exposed to the hazards associated with reenergizing the circuit or equipment are familiar with this procedure.
Working at Elevated Locations
Any person working on electrical equipment on a crane or other elevated must take necessary

GET INSTANT ACCESS
to THE MEMBERS LIBRARY
Safety materials created by safety professionals.
Access to the Safety Manager software.
Wide variety of safety videos and courses.
**Brand New** Safety Training Management System
Pre-Made Safety Materials Ready For Use
Created by experienced safety professionals & risk consultants. Saving you time, money, and risk of injuries.
95% of the work already done.
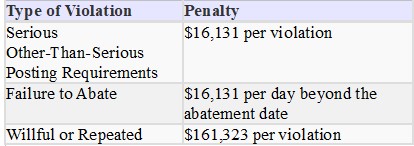
Below are the maximum penalty amounts, with the annual adjustment for inflation, that may be assessed after Jan. 15, 2024. (See OSHA Memo, Jan. 8, 2024).
**New OSHA HEAT 90 DAY**
>>Download Free HERE<<
**New 2024 OSHA 300 Form**
>>Download Free HERE<<
**Brand New**
Free with full membership subscription
Training LMS System
Ask The Safety Consultant
Safety Equipment Deal Finder

“SafetyInfo.com is the first go-to website for safety professionals and companies to use in establishing a solid safety program"
-Mike McKenzie, Certified Safety & Health Manager (CSHM), McSafety Solutions™
Note: You must have a full subscription to the Safety Library in order to use this material. Any use outside of your organization, for resell, or without an active membership is strictly prohibited and may result in prosecution under copyright infringement laws. Please contact us first, if you would be interested in reselling or using our materials for reproduction.
Inside the Members Library
Topic Index
Accident Prevention
Air Quality
Asbestos
Bloodborne Pathogens
Boilers
Chemical Safety
Compressed Gas
Confined Space
Construction
Construction Worksite
Cranes & Slings
Driver / Fleet Safety
Drug Free Workplace
Electrical
Emergency Management
Engineering Safety
Environmental
Equipment
Ergonomics
Fall Protection
Fire Safety & Prevention
First Aid
Flammable Materials
Forklifts
Hazard Communication
Hazardous Materials
Hearing Protection
Heat Stress
Hot Work
Housekeeping
Job Safety Analysis
Laboratory
Ladders
Lead
Lockout-Tagout
Machinery & Equipment
Material Handling
MSDS (SDS)
Medical & First Aid
Occupational Health
Office Safety
Off the Job Safety
Personal Protection
Process Safety
Record Keeping
Respiratory Protection
Silica Safety
Rules & Policies
Signs & Labels
Slips, Trips & Fall
Training
Terrorism Programs
Tool Safety
Vehicle & Driver
Violence Programs
Welding & Hot Work
Training Videos
Library Index
Training Materials
Videos/Courses
Talks
Articles
PowerPoint
Handouts
Training Overheads
Quizzes
Supervisor Briefs
Management Briefs
Safety Sessions
2 Minute OSHA Safety Talks
Pamphlets
First Aid Training
Supervisor Training
Hazardous Materials
Bomb Threat
Crossword Puzzles
Biological Agents
Forms & Documents
Forms
Checklists
Audit Guides
Inspections Guides
Signs & Labels
Environmental Audit Guides
Recordkeeping - OSHA 300
Sign & Label Maker
Safety Management Resources
Safety Manuals/Written Programs
Ergonomic Programs
Emergency Plans
Process Safety Management
Construction Safety
Occupational Health
Environmental
Topic Sheets
DOT Fleet-Driver
Hazardous Materials
Chemical Safety
Drug Free Workplace
Terrorism Programs
Development Guides
Safety Manager Software
Safety References & Graphics
Technical Safety Information
Posters
Topic & Fact Sheets
Development Information
Job Specific Safety Rules
Terrorism
Calculators
Safety Comic Strips
New Safety Training System
Schedule and train your employees with our materials. Add unlimited amount of employees. Record all progress and issue certificates. For group and individual training sessions.

