
Respiratory Protection - Respirator Safety
Respiratory Protection program, hazard assessment and selection of respiratory protective equipment is done in the same manner as for other types of personal protective equipment. In the control of those occupational diseases caused by breathing air contaminated with harmful dusts, fogs, fumes, mists, gases, smokes, sprays, or vapors, the primary objective should be to prevent atmospheric contamination. When effective engineering controls are not feasible, or while they are being instituted, appropriate respirators must be used. References: OSHA Standards Respiratory Protection (29 CFR 1910.134)
Respirator Type Pros & Con
This information presents advantages and disadvantages of various types of respiratory protection devices
Disposable Particulate Respirators
The NIOSH-certified disposable respirators labeled N, R, or P and may be obtained with or without exhalation valves. Most manufacturers also produce them in different sizes. A face shield may also be used in conjunction with a half-mask disposable respirator for protection against airborne flying material and fluids.
Advantages
1. The respirator is disposable and most models require no cleaning or maintenance.
2. The respirator is light weight and fairly comfortable to wear.
Assemble any equipment-audiovisuals, samples of PPE, handouts, etc.-in advance.
Disadvantages
1. The respirator is a negative-pressure device using the suction produced by inhalation to draw air through the filter. The inhalation process, even under the best of circumstances, will allow some contaminated air to leak into the facepiece.
2. A respirator with exhalation valves cannot be used when working in a cleanroom/sterile environments. The exhalation valve allows droplets and particles exhaled by the user to escape and potentially contaminate the work area. These respirators are also available without exhalation valves.
Replaceable Particulate Filter Respirators
Half-Mask Replaceable Particulate Filter Respirator
This respirator has single or dual filters made of the same material as the N, R, and P disposable respirators (HEPA filters can also be used). Most manufacturers produce more than one size. A face shield may also be used in conjunction with a half-mask particulate filter respirator.
Advantages
A. The respirator is lightweight and does not restrict mobility.
B. The respirator is made of rubber or elastomer and is durable. Only the filters need to be replaced when necessary.
Disadvantages
1. The respirator must be routinely inspected, cleaned, disinfected, and repaired.
2. The respirator is a negative-pressure device using the suction produced by inhalation to draw air through the filter. The inhalation process, even under the best of circumstances, will allow some contaminated air to leak into the facepiece.
3. Communication may be difficult.
4. The respirator cannot be used in areas where a clean or sterile field is required.
Full Face piece Replaceable Particulate Filter Respirator
The respirator can be equipped with the N, R, or P filters (HEPA filters can also be used). It is also manufactured in more than one size.
Advantages
1. The respirator provides a better seal than the half-mask and with HEPA or 100 series filter is more protective.
2. The respirator is durable.
3. The respirator provides eye protection.
Disadvantages
1. The respirator cannot be used in areas where a sterile field is required.
2. The respirator must be inspected, cleaned, and repaired.
3. The respirator is a negative-pressure device using the suction produced by inhalation to draw air through the filter. The inhalation process, even under the best of circumstances, will allow some contaminated air to leak into the facepiece.
4. Communication may be difficult.
5. Special lens kits are required for those respirator users who wear glasses.
Powered Air Purifying Respirators (PAPR)
Tight-Fitting PAPR
Equipment is battery operated, consists of a half or full facepiece, breathing tube, battery-operated blower, and particulate filters (HEPA only). A PAPR uses a blower to pass contaminated air through a HEPA filter, which removes the contaminant and supplies purified air to a facepiece. A PAPR is not a true positive-pressure device because it can be over-breathed when inhaling.
Advantages
1. The respirator is more protective than a half-mask respirator.
2. The respirator is usually more comfortable because air is forced into the mask by the blower, producing a cooling effect.
3. The respirator is durable.
4. Breathing resistance is lower.
Disadvantages
1. The respirator cannot be used where a clean or sterile field is required because it has an exhalation valve and in some cases air can exit around the face seal.
2. Batteries must be recharged and maintained to assure proper flow rates into the mask.
3. The respirator must be inspected, cleaned, and repaired.
4. Communication may be a problem.
5. A PAPR may be bulky and noisy.
Loose Fitting PAPR
This respirator consists of a hood or helmet, breathing tube, battery-operated blower, and HEPA filters.
Advantages
1. More protective than a half-mask respirator.
2. The respirator is more comfortable because it is loose-fitting.
3. Provides a cooling effect in the hood or helmet.
4. The respirator is durable.
5. Breathing resistance is lower.
6. Vision may be better.
7. Can be worn with facial hair as long as facial hair does not interfere with valve or function of the respirator.
Disadvantages
1. The equipment cannot be used where a sterile field must be maintained because air exits around the hood or helmet.
2. Batteries must be charged and maintained.
3. The respirator must be inspected, cleaned, and repaired.
4. Communication may be difficult.
5. A PAPR may be bulky and noisy.
Positive-Pressure Supplied-Air Respirators
Fixed Air Supply
Supplied-air respirators use compressed air from a stationary source delivered through a hose under pressure to a half-mask or a full facepiece. A face shield may also be used in conjunction with a half-mask airline respirator for protection against body fluids.
Advantages
1. The respirator is much more protective because it provides positive pressure in the facepiece and almost all leakage is outward. A positive-pressure supplied-air respirator should be used when disposable respirators, replaceable respirators, or PAPRs do not provide adequate protection.
2. Breathing resistance is minimal.
3. The respirator is relatively comfortable to wear.
Disadvantages
1. The airline hose restricts the user's mobility.
2. This respirator exhausts air contaminated by the user and should not be worn during clean or sterile procedures.
3. The respirator must be inspected, cleaned, and repaired.
4. Communication may be difficult.
5. Requires installation and maintenance of a regulated compressed air supply for Grade D breathing air.
6. Maintenance requires highly skilled, technically trained personnel.
7. Length of hose and connection point must be adequate to prevent exposure to airborne contaminates when removing the respirator.
Pressure Demand - Air Tank Supplied Respirators
This equipment is generally referred to as Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus (SCBA). The user dons a harness that supports a breathing air tank and pressure regulator devices. Full face masks are used with this type equipment. Used for emergency response situations.
Advantages
1. The respirator provides for mobility and may be used in a forced-air mode.
2. Allows personnel to work in areas in which filter respirators would not provide protection.
3. Breathing resistance is minimal in forced-air mode.
4. Allows user to enter and exit contaminated areas without disconnecting from air source
Disadvantages
1. The tank and harness is heavy.
2. Limited use time based on exhaustion of tank air supply.
3. This respirator exhausts air contaminated by the user and should not be worn during clean or sterile procedures.
4. The respirator must be inspected, cleaned, and repaired.
5. Communication may be difficult.
6. Requires installation and maintenance of a regulators and compressed air tanks with Grade D breathing air.
7. Maintenance requires highly skilled, technically trained personnel.
OSHA requires that voluntary use of respirators, when not required by an employer, must be controlled as strictly as under required circumstances. To prevent violations of the Respiratory Protection Standard Employees should not be allowed voluntary use of their own or company supplied respirators unless they are under the full control of the Respiratory Protection Program.
Respiratory Protection Program Evaluation
Evaluations of the workplace are necessary to ensure that the written respiratory protection program is being properly implemented, this includes consulting with employees to ensure that they are using the respirators properly. Evaluations should be conducted to ensure that the provisions of the current written program are being effectively implemented and that it continues to be effective Program evaluation includes discussions with employees required to use respirators to assess the employees' views on program effectiveness and to identify any problems. Factors to be assessed include, but are not limited to:
Appropriate respirator selection for the hazards to which the employee is exposed;
Proper respirator use under the workplace conditions the employee encounters; and proper respirator maintenance.
Selection of Respirators
Respiratory hazards in each workplace, must be identified and relevant workplace and user factors and Assigned Protection Factors must be used as a basis for respirator selections. Include estimates of employee exposures to respiratory hazards and an identification of the contaminant's chemical state and physical form. All selected respirators must be NIOSH-certified .
No respirator can provide 100% effectiveness. OSHA has implemented Assigned Protection Factors (APFs) for various types of respirators. The purpose of APFs is to ensure use of respirators does not cause over-exposure to specific contaminants. Maximum permissible exposure levels (PEL) are generally based on specific concentrations over an 8 hour daily period without using a respirator.
All materials in the members area for this topic index

GET INSTANT ACCESS
to THE MEMBERS LIBRARY
Safety materials created by safety professionals.
Access to the Safety Manager software.
Wide variety of safety videos and courses.
**Brand New** Safety Training Management System
Pre-Made Safety Materials Ready For Use
Created by experienced safety professionals & risk consultants. Saving you time, money, and risk of injuries.
95% of the work already done.
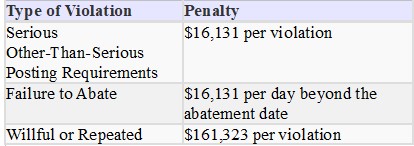
Below are the maximum penalty amounts, with the annual adjustment for inflation, that may be assessed after Jan. 15, 2024. (See OSHA Memo, Jan. 8, 2024).
**New OSHA HEAT 90 DAY**
>>Download Free HERE<<
**New 2024 OSHA 300 Form**
>>Download Free HERE<<
**Brand New**
Free with full membership subscription
Training LMS System
Ask The Safety Consultant
Safety Equipment Deal Finder

“SafetyInfo.com is the first go-to website for safety professionals and companies to use in establishing a solid safety program"
-Mike McKenzie, Certified Safety & Health Manager (CSHM), McSafety Solutions™
Note: You must have a full subscription to the Safety Library in order to use this material. Any use outside of your organization, for resell, or without an active membership is strictly prohibited and may result in prosecution under copyright infringement laws. Please contact us first, if you would be interested in reselling or using our materials for reproduction.
Inside the Members Library
Topic Index
Accident Prevention
Air Quality
Asbestos
Bloodborne Pathogens
Boilers
Chemical Safety
Compressed Gas
Confined Space
Construction
Construction Worksite
Cranes & Slings
Driver / Fleet Safety
Drug Free Workplace
Electrical
Emergency Management
Engineering Safety
Environmental
Equipment
Ergonomics
Fall Protection
Fire Safety & Prevention
First Aid
Flammable Materials
Forklifts
Hazard Communication
Hazardous Materials
Hearing Protection
Heat Stress
Hot Work
Housekeeping
Job Safety Analysis
Laboratory
Ladders
Lead
Lockout-Tagout
Machinery & Equipment
Material Handling
MSDS (SDS)
Medical & First Aid
Occupational Health
Office Safety
Off the Job Safety
Personal Protection
Process Safety
Record Keeping
Respiratory Protection
Silica Safety
Rules & Policies
Signs & Labels
Slips, Trips & Fall
Training
Terrorism Programs
Tool Safety
Vehicle & Driver
Violence Programs
Welding & Hot Work
Training Videos
Library Index
Training Materials
Videos/Courses
Talks
Articles
PowerPoint
Handouts
Training Overheads
Quizzes
Supervisor Briefs
Management Briefs
Safety Sessions
2 Minute OSHA Safety Talks
Pamphlets
First Aid Training
Supervisor Training
Hazardous Materials
Bomb Threat
Crossword Puzzles
Biological Agents
Forms & Documents
Forms
Checklists
Audit Guides
Inspections Guides
Signs & Labels
Environmental Audit Guides
Recordkeeping - OSHA 300
Sign & Label Maker
Safety Management Resources
Safety Manuals/Written Programs
Ergonomic Programs
Emergency Plans
Process Safety Management
Construction Safety
Occupational Health
Environmental
Topic Sheets
DOT Fleet-Driver
Hazardous Materials
Chemical Safety
Drug Free Workplace
Terrorism Programs
Development Guides
Safety Manager Software
Safety References & Graphics
Technical Safety Information
Posters
Topic & Fact Sheets
Development Information
Job Specific Safety Rules
Terrorism
Calculators
Safety Comic Strips
New Safety Training System
Schedule and train your employees with our materials. Add unlimited amount of employees. Record all progress and issue certificates. For group and individual training sessions.

