
OSHA Safety Program - Crane & Hoist Safety
Purpose
Many types of cranes, hoists, and rigging devices are used at [COMPANY] for lifting and moving materials. [COMPANY]'s policy is to maintain a safe workplace for its employees; therefore, it cannot be overemphasized that only qualified and licensed individuals shall operate these devices. The safety rules and guidance in this chapter apply to all operations at [COMPANY] that involve the use of cranes and hoists installed in or attached to buildings and to all [COMPANY] employees, supplemental labor, and subcontractor personnel who use such devices.
Responsibilities
Supervisors are responsible for:
• Ensuring that employees under their supervision receive the required training and are certified and licensed to operate the cranes and hoists in their areas.
• Providing training for prospective crane and hoist operators. This training must be conducted by a qualified, designated instructor who is a licensed crane and hoist operator and a full-time [COMPANY] employee.
• Evaluating crane and hoist trainees using the Crane Safety Checklist and submitting the Qualification Request Form to the Safety Office to obtain the operator's license.
• Ensuring that hoisting equipment is inspected and tested monthly by a responsible individual and that rigging equipment is inspected annually.
Crane and Hoist Operators are responsible for:
• Operating hoisting equipment safely.
• Conducting functional tests prior to using the equipment.
• Selecting and using rigging equipment appropriately.
• Having a valid operator's license on their person while operating cranes or hoists.
• Participating in the medical certification program, as required.
Engineering/Maintenance/Operations Department is responsible for:
• Performing annual maintenance and inspection of all [COMPANY] cranes and hoists that are not covered by a program with maintenance responsibility.
• Conducting periodic and special load tests of cranes and hoists.
• Maintaining written records of inspections and tests, and providing copies of all inspections and test results to facility managers and building coordinators who have cranes and hoists on file.
• Inspecting and load testing cranes and hoists following modification or extensive repairs (e.g., a replaced cable or hook, or structural modification.)
• Scheduling a non-destructive test and inspection for crane and hoist hooks at the time of the periodic load test, and testing and inspecting before use new replacement hooks and other hooks suspected of having been overloaded. The evaluation, inspection, and testing may include, but are not limited to visual, dye penetrant, and magnetic particle techniques referenced in ASME B30.10 (Hooks, Inspection and Testing.)
• Maintaining all manuals for cranes and hoists in a central file for reference.
Safety Department is responsible for:
• Conducting training for all Crane & Hoist Operators
• Issuing licenses to Crane and Hoist Operators
• Periodically verifying monthly test and inspection reports.
• Interpreting crane and hoist safety rules and standards.
Safe Operating Requirements
All workers who use any [COMPANY] crane or hoist shall have an operator's license. The company issues licenses for authorized employees who have been specifically trained in crane and hoist operations and equipment safety.
Crane and Hoist Operators
To be qualified as a Crane and Hoist Operator, the candidate shall have received hands-on training from a licensed, qualified crane and hoist operator designated by the candidate's supervisor. Upon successful completion of training, the licensed crane and hoist operator and the candidate's supervisor will fill out and sign the Qualification Request Form and Crane Safety Checklist and send them to the Safety Office for approval. The candidate will be issued a license upon approval by the Safety Manager. Crane and Hoist Operators must renew their license every three years by satisfying the requirements described above.
Crane and Hoist Safety Design Requirements
Following are the design requirements for cranes and hoists and their components:
• The design of all commercial cranes and hoists shall comply with the requirements of ASME/ANSI B30 standards and Crane Manufacturer's Association of America standards (CMAA-70 and CMAA-74). [COMPANY]-fabricated lifting equipment shall comply with the requirements in Chapter 2.2 (Lifting Equipment) of Mechanical Engineering Design Safety Standards (latest edition).
• All crane and hoist hooks shall have safety latches.
• Hooks shall not be painted (or re-painted) if the paint previously applied by the manufacturer is worn.
• Crane pendants shall have an electrical disconnect switch or button to open the main-line control circuit.
• Cranes and hoists shall have a main electrical disconnect switch. This switch shall be in a separate box that is labeled with lockout capability.
• Crane bridges and hoist monorails shall be labeled on both sides with the maximum capacity.
• Each hoist-hook block shall be labeled with the maximum hook capacity.
• Directional signs indicating N-W-S-E shall be displayed on the bridge underside, and a corresponding directional label shall be placed on the pendant.
• A device such as an upper-limit switch or slip clutch shall be installed on all building cranes and hoists. A lower-limit switch may be required when there is insufficient hoist rope on the drum to reach the lowest point.
• All cab and remotely operated bridge cranes shall have a motion alarm to signal bridge movement.
• All newly installed cranes and hoists, or those that have been extensively repaired or rebuilt structurally, shall be load tested at 125% capacity prior to being placed into service.
• If an overload device is installed, a load test to the adjusted setting is required.
• Personnel baskets and platforms suspended from any crane shall be designed in accordance with the specifications in 29 CFR 1926.550(g).
General Safety Rules
Operators shall comply with the following rules while operating the cranes and hoists:
• Do not engage in any practice that will divert your attention while operating the crane.
• Respond to signals only from the person who is directing the lift, or any appointed signal person. Obey a stop signal at all times, no matter who gives it.
• Do not move a load over people. People shall not be placed in jeopardy by being under a suspended load. Also, do not work under a suspended load unless the load is supported by blocks, jacks, or a solid footing that will safely support the entire weight. Have a crane or hoist operator remain at the controls or lock open and tag the main electrical disconnect switch.
• Ensure that the rated load capacity of a crane's bridge, individual hoist, or any sling or fitting is not exceeded. Know the weight of the object being lifted or use a dynamometer or load cell to determine the weight.
• Check that all controls are in the OFF position before closing the main-line disconnect switch.
• If spring-loaded reels are provided to lift pendants clear off the work area, ease the pendant up into the stop to prevent damaging the wire.
• Avoid side pulls. These can cause the hoist rope to slip out of the drum groove, damaging the rope or destabilizing the crane or hoist.
• To prevent shock loading, avoid sudden stops or starts. Shock loading can occur when a suspended load is accelerated or decelerated, and can overload the crane or hoist. When completing an upward or downward motion, ease the load slowly to a stop.
Operation Rules
Pre-operational Test
At the start of each work shift, operators shall do the following steps before making lifts with any crane or hoist:
1. Test the upper-limit switch. Slowly raise the unloaded hook block until the limit switch trips.
2. Visually inspect the hook, load lines, trolley, and bridge as much as possible from the operator's station; in most instances, this will be the floor of the building.
3. If provided, test the lower-limit switch.
4. Test all direction and speed controls for both bridge and trolley travel.
5. Test all bridge and trolley limit switches, where provided, if operation will bring the equipment in close proximity to the limit switches.
6. Test the pendant emergency stop.
7. Test the hoist brake to verify there is no drift without a load.
8. If provided, test the bridge movement alarm.
9. Lock out and tag for repair any crane or hoist that fails any of the above tests.
Moving a Load
• Center the hook over the load to keep the cables from slipping out of the drum grooves and overlapping, and to prevent the load from swinging when it is lifted. Inspect the drum to verify that the cable is in the grooves.
• Use a tag line when loads must traverse long distances or must otherwise be controlled. Manila rope may be used for tag lines.
• Plan and check the travel path to avoid personnel and obstructions.
• Lift the load only high enough to clear the tallest obstruction in the travel path.
• Start and stop slowly.
• Land the load when the move is finished. Choose a safe landing.
• Never leave suspended loads unattended. In an emergency where the crane or hoist has become inoperative, if a

GET INSTANT ACCESS
to THE MEMBERS LIBRARY
Safety materials created by safety professionals.
Access to the Safety Manager software.
Wide variety of safety videos and courses.
**Brand New** Safety Training Management System
Pre-Made Safety Materials Ready For Use
Created by experienced safety professionals & risk consultants. Saving you time, money, and risk of injuries.
95% of the work already done.
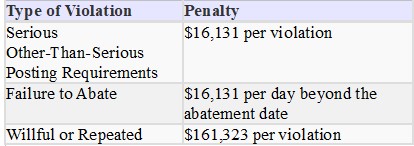
Below are the maximum penalty amounts, with the annual adjustment for inflation, that may be assessed after Jan. 15, 2024. (See OSHA Memo, Jan. 8, 2024).
**New OSHA HEAT 90 DAY**
>>Download Free HERE<<
**New 2024 OSHA 300 Form**
>>Download Free HERE<<
**Brand New**
Free with full membership subscription
Training LMS System
Ask The Safety Consultant
Safety Equipment Deal Finder

“SafetyInfo.com is the first go-to website for safety professionals and companies to use in establishing a solid safety program"
-Mike McKenzie, Certified Safety & Health Manager (CSHM), McSafety Solutions™
Note: You must have a full subscription to the Safety Library in order to use this material. Any use outside of your organization, for resell, or without an active membership is strictly prohibited and may result in prosecution under copyright infringement laws. Please contact us first, if you would be interested in reselling or using our materials for reproduction.
Inside the Members Library
Topic Index
Accident Prevention
Air Quality
Asbestos
Bloodborne Pathogens
Boilers
Chemical Safety
Compressed Gas
Confined Space
Construction
Construction Worksite
Cranes & Slings
Driver / Fleet Safety
Drug Free Workplace
Electrical
Emergency Management
Engineering Safety
Environmental
Equipment
Ergonomics
Fall Protection
Fire Safety & Prevention
First Aid
Flammable Materials
Forklifts
Hazard Communication
Hazardous Materials
Hearing Protection
Heat Stress
Hot Work
Housekeeping
Job Safety Analysis
Laboratory
Ladders
Lead
Lockout-Tagout
Machinery & Equipment
Material Handling
MSDS (SDS)
Medical & First Aid
Occupational Health
Office Safety
Off the Job Safety
Personal Protection
Process Safety
Record Keeping
Respiratory Protection
Silica Safety
Rules & Policies
Signs & Labels
Slips, Trips & Fall
Training
Terrorism Programs
Tool Safety
Vehicle & Driver
Violence Programs
Welding & Hot Work
Training Videos
Library Index
Training Materials
Videos/Courses
Talks
Articles
PowerPoint
Handouts
Training Overheads
Quizzes
Supervisor Briefs
Management Briefs
Safety Sessions
2 Minute OSHA Safety Talks
Pamphlets
First Aid Training
Supervisor Training
Hazardous Materials
Bomb Threat
Crossword Puzzles
Biological Agents
Forms & Documents
Forms
Checklists
Audit Guides
Inspections Guides
Signs & Labels
Environmental Audit Guides
Recordkeeping - OSHA 300
Sign & Label Maker
Safety Management Resources
Safety Manuals/Written Programs
Ergonomic Programs
Emergency Plans
Process Safety Management
Construction Safety
Occupational Health
Environmental
Topic Sheets
DOT Fleet-Driver
Hazardous Materials
Chemical Safety
Drug Free Workplace
Terrorism Programs
Development Guides
Safety Manager Software
Safety References & Graphics
Technical Safety Information
Posters
Topic & Fact Sheets
Development Information
Job Specific Safety Rules
Terrorism
Calculators
Safety Comic Strips
New Safety Training System
Schedule and train your employees with our materials. Add unlimited amount of employees. Record all progress and issue certificates. For group and individual training sessions.

