
Compressed Gas Safety
Compressed gases and cylinders must be properly stored, transported and used to prevent injury and accidents. Industrial gas cylinders are color coded to provide identification "at a glance". Regulators, cylinders and cylinder valves must be inspected regularly to ensure safe operation. Gases that may react with each other must be stored separately.
Compressed gas cylinders present numerous hazards and can contain gases that are:
• Flammable or combustible
• Explosive
• Corrosive
•Poisonous
Compressed Gas Cylinder Safety Precautions
Gas cylinders must be clearly identified. Never rely on the color of the cylinder for identification.
• Never attempt to repair a cylinder or valve
• Firmly attach cylinders to a bench top, wall, or holding cage. Use chains or sturdy straps
• Shut the cylinder valve when gas is not in use
• Open cylinder valves slowly. Never fully open cylinder cylinder valves.
• Don't store acetylene cylinders on their side
• Maintain 20 feet between flammable gas cylinders and oxygen cylinders
• Never bleed a cylinder below 25 psi.
• Close all valves and replace caps before moving
• Store empty and full cylinders in separate areas
• Use safety glasses or face shield when handling or connecting gas cylinders
• Never roll or drag cylinders
• Use wheeled carts to move larger cylinders
• Move only one cylinder at a time
Understanding the hazards
While each type of compressed gas has its own hazards, most are flammable, explosive, toxic, or a combination of these types. Some common kinds of compressed gas include acetylene, ammonia, carbon dioxide, chlorine, fluorine, hydrogen and oxygen. Remind your employees to read the label on the cylinder and the material safety data sheet (MSDS) for safety information.
Safe steps
Here are recommended safe practices when handling most compressed gas cylinders:
How to store them:
• Cylinders should be stored in a dry, well-ventilated area at least 20 feet from combustible materials. Don't keep the cylinders in lockers or cupboards.
• Oxygen cylinders must be separated by 20 feet from fuel-gas cylinders, such as acetylene. or by a non-combustible barrier at least 5 feet high with a fire-resistance rating of at least one-half hour.
• They should be stored upright and secured with a chain or cable.
• Valves and caps should be completely closed.
• Room temperature should remain constant.
How to transport them:
• Secure the cylinders upright.
• Don't drag them—use a hand truck.
• Handle carefully—avoid dropping or banging them.
How to use them:
• Open valves by hand, rather than with a tool (unless a specific tool is recommended by the supplier).
• Release the valves slowly.
• If a special wrench is required to open the valve, leave it in position while in use so that the flow of gas can be stopped quickly in an emergency.
• Don't tamper with safety devices.
• Keep cylinders upright and away from heat, sparks, fire, or electrical circuits.
• Avoid getting any oil or grease on the cylinders, particularly those containing oxygen.
How to maintain them:
• All cylinders should be properly marked to identify the contents.
• Make sure valve protection caps are in place.
• If cylinders are leaking, take them outdoors away from sparks or heat and slowly empty them.
• Make sure to mark all empty cylinders (some companies use "MT").
• Put a warning tag on cylinders that were leaking and notify the supplier.
Other precautions:
• Never mix gases in a cylinder or try to refill a cylinder (contact the supplier).
• If a cylinder leaks or a valve is broken, tag the cylinder and contact a trained maintenance person or the supplier.
• NEVER smoke around a compressed gas cylinder.
• Don't use the recessed top of the cylinder as a storage area for tools or material.
Compressed Gas Cylinder Safety Training Tips
When conducting your training session, have a compressed gas cylinder available and demonstrate proper handling and operating procedures. Show what a damaged or leaking cylinder looks like and explain how to report these conditions. Review relevant MSDS's and discuss health hazards and safety precautions. Ask about any problems with transporting or storing cylinders at your facility.
In particular, warn your employees not to become complacent around compressed gas cylinders. If your workers are at all skeptical about the need to use caution, remind them of the story of the runaway cylinder that wreaked havoc.
All materials in the members area for this topic index

GET INSTANT ACCESS
to THE MEMBERS LIBRARY
Safety materials created by safety professionals.
Access to the Safety Manager software.
Wide variety of safety videos and courses.
**Brand New** Safety Training Management System
Pre-Made Safety Materials Ready For Use
Created by experienced safety professionals & risk consultants. Saving you time, money, and risk of injuries.
95% of the work already done.
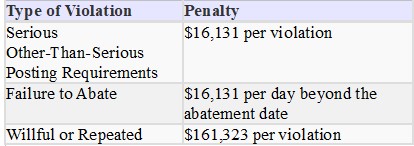
Below are the maximum penalty amounts, with the annual adjustment for inflation, that may be assessed after Jan. 15, 2024. (See OSHA Memo, Jan. 8, 2024).
**New OSHA HEAT 90 DAY**
>>Download Free HERE<<
**New 2024 OSHA 300 Form**
>>Download Free HERE<<
**Brand New**
Free with full membership subscription
Training LMS System
Ask The Safety Consultant
Safety Equipment Deal Finder

“SafetyInfo.com is the first go-to website for safety professionals and companies to use in establishing a solid safety program"
-Mike McKenzie, Certified Safety & Health Manager (CSHM), McSafety Solutions™
Note: You must have a full subscription to the Safety Library in order to use this material. Any use outside of your organization, for resell, or without an active membership is strictly prohibited and may result in prosecution under copyright infringement laws. Please contact us first, if you would be interested in reselling or using our materials for reproduction.
Inside the Members Library
Topic Index
Accident Prevention
Air Quality
Asbestos
Bloodborne Pathogens
Boilers
Chemical Safety
Compressed Gas
Confined Space
Construction
Construction Worksite
Cranes & Slings
Driver / Fleet Safety
Drug Free Workplace
Electrical
Emergency Management
Engineering Safety
Environmental
Equipment
Ergonomics
Fall Protection
Fire Safety & Prevention
First Aid
Flammable Materials
Forklifts
Hazard Communication
Hazardous Materials
Hearing Protection
Heat Stress
Hot Work
Housekeeping
Job Safety Analysis
Laboratory
Ladders
Lead
Lockout-Tagout
Machinery & Equipment
Material Handling
MSDS (SDS)
Medical & First Aid
Occupational Health
Office Safety
Off the Job Safety
Personal Protection
Process Safety
Record Keeping
Respiratory Protection
Silica Safety
Rules & Policies
Signs & Labels
Slips, Trips & Fall
Training
Terrorism Programs
Tool Safety
Vehicle & Driver
Violence Programs
Welding & Hot Work
Training Videos
Library Index
Training Materials
Videos/Courses
Talks
Articles
PowerPoint
Handouts
Training Overheads
Quizzes
Supervisor Briefs
Management Briefs
Safety Sessions
2 Minute OSHA Safety Talks
Pamphlets
First Aid Training
Supervisor Training
Hazardous Materials
Bomb Threat
Crossword Puzzles
Biological Agents
Forms & Documents
Forms
Checklists
Audit Guides
Inspections Guides
Signs & Labels
Environmental Audit Guides
Recordkeeping - OSHA 300
Sign & Label Maker
Safety Management Resources
Safety Manuals/Written Programs
Ergonomic Programs
Emergency Plans
Process Safety Management
Construction Safety
Occupational Health
Environmental
Topic Sheets
DOT Fleet-Driver
Hazardous Materials
Chemical Safety
Drug Free Workplace
Terrorism Programs
Development Guides
Safety Manager Software
Safety References & Graphics
Technical Safety Information
Posters
Topic & Fact Sheets
Development Information
Job Specific Safety Rules
Terrorism
Calculators
Safety Comic Strips
New Safety Training System
Schedule and train your employees with our materials. Add unlimited amount of employees. Record all progress and issue certificates. For group and individual training sessions.

